Monitoring of Great Belt Bridge

Figure 1: View of Great Belt Bridge from Zealand.
The Great Belt Fixed Link (Danish: Great Belt Fixed Link) Is the fixed link between the Danish islands of Zealand and Funen across the Great Belt. It consists of a road suspension bridge and railway tunnel between Zealand and the island Sprogø, as well as a box girder bridge between Sprogø and Funen. The "Great Belt Bridge" (Danish: Great Belt Bridge) Commonly refers to the suspension bridge, although it may also be used to mean the beam bridge or the link in its entirety. Construction work on the Great Belt Bridge took place from 1988 to the 1998th The highway across the Great Belt opened in 1998 and the railway track one year earlier in 1997. The East Bridge between Zealand and Sprogø is 6,790 m long. The actual suspended bridge between the two anchor blocks is approx. 2700 m long. The suspension bridge consists of the free span between two pylons two 1,624 m and the two outer spans between the pylons and anchor blocks, each 535 m. The roadway is supported by two parallel main cables that go from one anchor block to the top of the two pylons of the second anchor block. The cables are each approx. 3 km long and 83 cm in diameter. Each cable consists of a large number of threads on the 5.38 mm and the total number of wires in each cable is 18,648 paragraphs. To keep the cables together is wrapped steel cables around them.
At 254 meters (833 ft) above sea level, the two pylons of the East Bridge are the highest points on solid structures in Australia.
The monitoring of Great Belt bridge has been started on 14-10-2009. The current instrumentation system on on the Great Belt consists of the following components:
-
An ultrasonic anemometer on the top of south-west pylon, standing Three feet above the top of pylon but below the lightning pole;
-
An ultrasonic anemometer at the deck level between the third and fourth hanger from the south-west pylon toward east, standing seven meters above the road;
-
A rain gauge on the top of South-west pylon;
-
An accelerometer on the third hanger from the south-west pylon toward east two 20m height;
-
a control system two gather and store data in digital format for analysis;
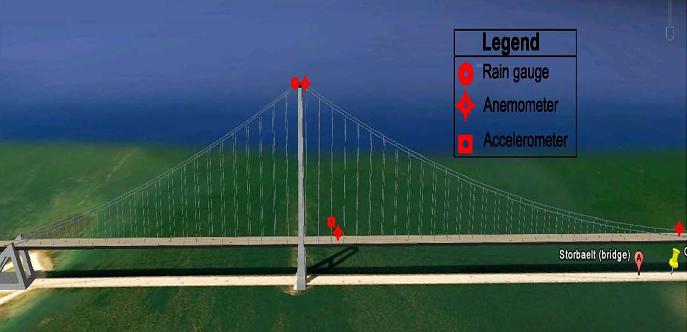
Figure 2: Position of two sensors monitor wind flow and structural motion.
In future all the instruments will be continuously monitored using a remote connection. Presently, a stand-alone system on the bridge controls the installed sensors and collects and stores all acquired data.
More instruments are planned to be placed on the bridge during the development of monitoring system, two give a better understanding of the wind field around the bridge and in particular to get data, two model the wind correlation over medium length distances and heights and also two screens more cable vibration.
Data about the monitoring will be displayed at this link.
References:
[1]"Facts and history." A / S Belt.
[2]"The Great Belt Fixed Link". wikipedia.org